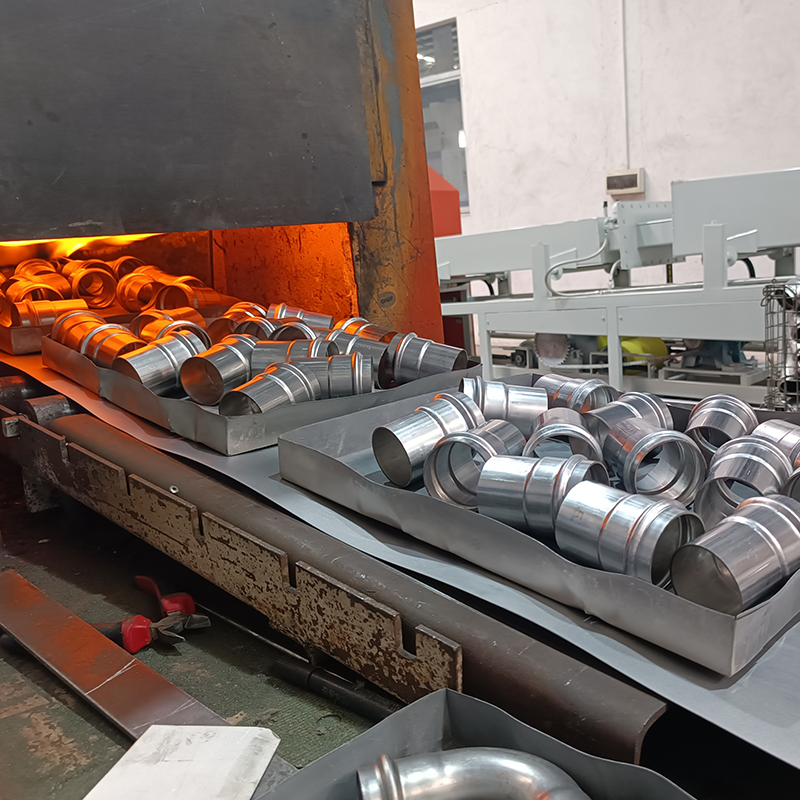
What heat treatments are required for stainless steel 316 straight pipe fittings
May. 31, 2025
Common types of heat treatments for stainless steel 316 straight pipe fittings include solution treatment, stabilization treatment, and stress-relief treatment. Here are detailed introductions:
Solution Treatment:
Purpose: Heat the stainless steel pipe fittings to the austenite region to fully dissolve chromium and other alloy elements in the steel, obtaining a single austenite structure, eliminating internal stresses in the steel, and improving its plasticity and toughness.
Process Parameters: The temperature is typically between 1050-1150°C. The holding time depends on the material thickness, generally requiring 1 hour for every 25 mm of thickness, followed by rapid cooling to room temperature. Methods such as water quenching, oil quenching, or air cooling can be employed.
Stabilization Treatment:
Purpose: Conducted after solution treatment, it aims to ensure the uniform distribution of carbon, nitrogen, and other elements in the austenite, preventing the precipitation of unstable phases such as carbides and nitrides during subsequent cooling. This further enhances the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of the steel.
Process Parameters: The steel is usually heated to 850-880°C, held at that temperature, and then air-cooled.
Stress-Relief Treatment:
Purpose: Eliminate residual stresses in the steel after cold working or welding to improve its stability and corrosion resistance. This treatment is typically performed after the pipe fittings have been machined to reduce deformation and prevent issues such as cracking.
Process Parameters: Generally, the steel is heated to 300-350°C for tempering. For steels that do not contain stabilizing elements such as Ti and Nb, the heating temperature should not exceed 450°C to avoid precipitation of chromium carbides, which could cause intergranular corrosion. For cold-worked and welded parts of ultra-low carbon and Ti, Nb-containing stainless steels, heating at 500-950°C followed by slow cooling is required.