What heat treatment is required for iron nails
Dec. 11, 2025
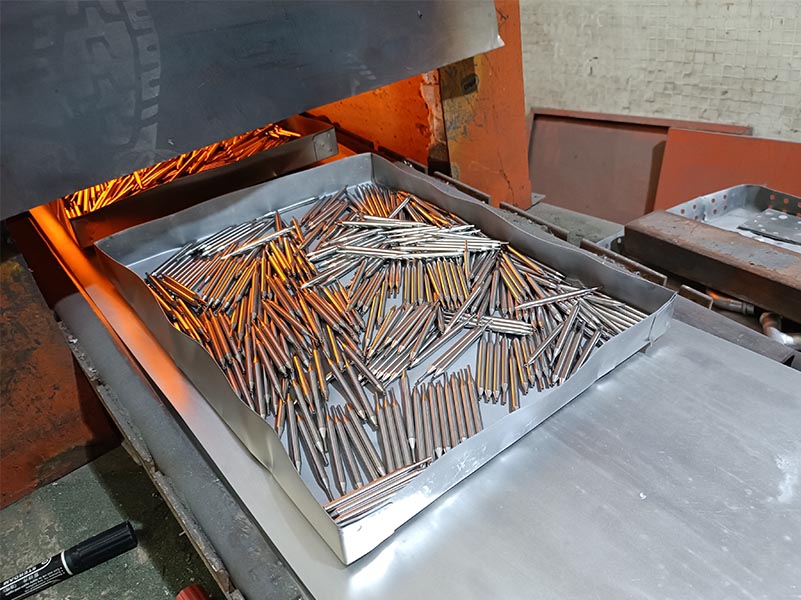
The heat treatment process for iron nails should be selected based on their specific applications and performance requirements. Common treatment methods include annealing, quenching, tempering, etc. The following outlines the applications and functions of different heat treatment processes in iron nail production:
Annealing
Purpose: To eliminate internal stresses generated during cold working (such as wire drawing and stamping) of iron nails, reduce hardness, and improve plasticity and toughness for easier subsequent processing (such as cutting and bending).
Process: Heat the iron nails to a temperature above the critical temperature (Ac₁ or Ac₃), hold for a certain period, and then cool slowly (furnace cooling or air cooling).
Applicable Scenarios:
Pretreatment of raw materials (such as steel wire) before iron nail production.
Quenching
Purpose: To achieve high hardness and wear resistance in iron nails through rapid cooling (such as water quenching or oil quenching).
Process:
Heat to a temperature above the critical temperature (complete austenitization).
Quickly immerse in a quenching medium (such as water or oil) for cooling.
Applicable Scenarios:
Iron nails requiring high hardness (such as industrial nails and concrete nails).
Tempering
Purpose: To eliminate internal stresses generated during quenching, adjust the balance between hardness and toughness, and prevent brittle fracture.
Process: Heat the quenched iron nails to a temperature below the critical temperature (150-650°C), hold, and then cool.
Applicable Scenarios:
An essential process after quenching to ensure that iron nails possess both hardness and toughness during use.
Surface Hardening Treatment (Optional)
Purpose: To harden only the surface of iron nails while maintaining the toughness of the core, suitable for high-wear scenarios.
Common Methods:
Induction quenching: Heat the surface with high-frequency current and cool rapidly.
Carburizing/Nitriding: Form a hard layer on the surface through chemical heat treatment.
Applicable Scenarios:
Surface strengthening of iron nails for special purposes (such as woodworking nails and mining nails).
Process Selection Recommendations
High-hardness iron nails: Quenching + tempering (such as concrete nails).
Easily processable iron nails: Annealing (to reduce hardness and facilitate stamping).
Surface wear-resistant iron nails: Surface hardening treatment (such as induction quenching).